- Alessandro Chiola is an architect at BPTW, one of our Festival Club members. His piece was one of 2 chosen entries selected by the practice following an internal ‘Boundaries’ competition run for its staff. In this essay, Alessandro discusses the boundaries facing housing estates today, and the role of regeneration projects in overcoming these.

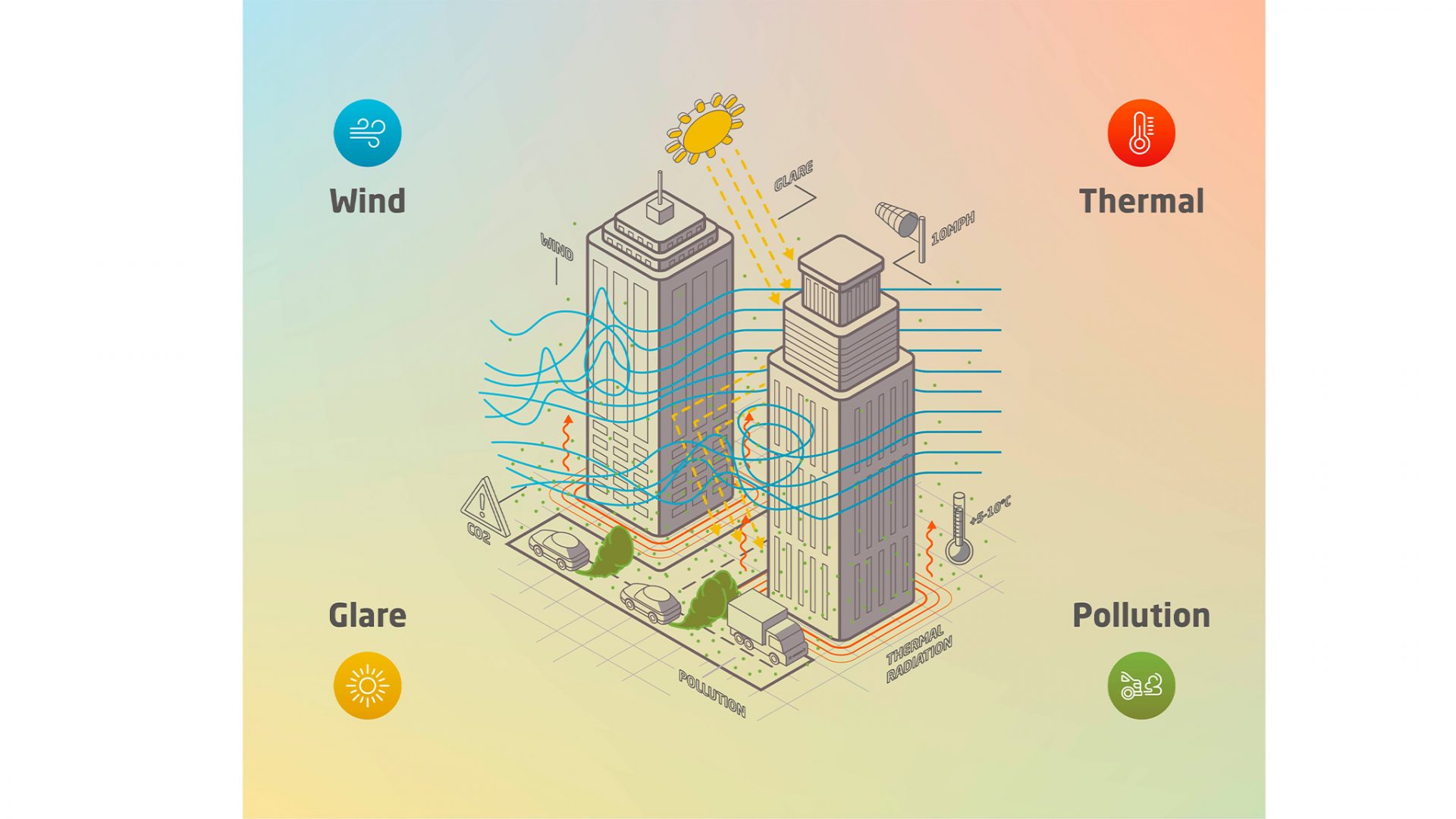
Social housing estates are not always well-integrated into their context, and in many cases, are configured as islands, separated from the surrounding area. This isolation of public estates can be traced back to two main ‘boundaries’:urban & architectural, and social & mental.
Urban & architectural boundaries
Every estate is shaped by a different array of design decisions, many of which have a lasting impact on how isolated these neighbourhoods become. These include:
- The estate’s proximity to the inner-city
- A lack of strategic connection with the surrounding urban grain
- A sense of mono-functionality, which leaves the neighbourhoods as ‘dormitories’
- A lack of permeability, as often only residents are interested in engaging with the estate
- Infrastructure, including streets, bridges and railways, as well as other physical barriers, such as gates and fences
- Topographical barriers, such as a difference in level or unsuccessful landscaping
- Spatial continuity and landscape coherency, such as usability and land use
Social & mental boundaries
“[…] Since council housing has come to mean housing for the working class, the wall exists unbroken throughout every estate in the land. The wall may be invisible […] The wall in the head is built up slowly over the course of a lifetime […] If your family and friends all live in the same estate, that’s a little wall built for you right there. If you have links outside it […] you’ve one less wall to knock down.”
In her book ‘Estates:An Intimate History’, Lynsey Hanley gives an overview of the difficulties that many people living in council estates, face today. Born and raised in a Birmingham council estate, she tells the story of the estate and the people who live there from her own experience, challenging the stigma that otherwise surrounds the idea of council estates. Hanley goes on to describe how the absence of permeability or a relationship with the rest of the city often creates segregation within the estate itself, with the residents living in isolation and having little involvement in daily neighbourhood life.
A lack of social diversity may also have an impact on the isolating nature of estates. With these communities often finding themselves on the edge of society and struggling to have an active voice in local decision making, the estate environment further limits the social exchanges and activities that expose people to new experiences, deepening the rift between the estates and the nearby cities. To tackle this isolation, it is therefore not only the physical boundaries that need to be overcome, but also the mental boundaries that have become ingrained within the estate. This can take the form of promoting reciprocal interaction and encouraging people to engage and interact their whole neighbourhood, improving the functionality of estates and their connections with the city and in turn reducing the likelihood of these becoming a separated enclave.
For this to be successful, housing regeneration projects must approach this urban and social isolation from a wider perspective, which considers the surrounding context. Prioritising the transition between public, semi-public and private spaces, creates the opportunity to re-establish streets and routes as connections, creating new public areas as a setting for organic encounters. This offers a sense of openness, social mix and new uses and activities ,which helps welcome residents from other neighbourhoods to these estates. Creating a meaningful reason to engage with these council estates will eventually help to break down the stigmas surrounding them.
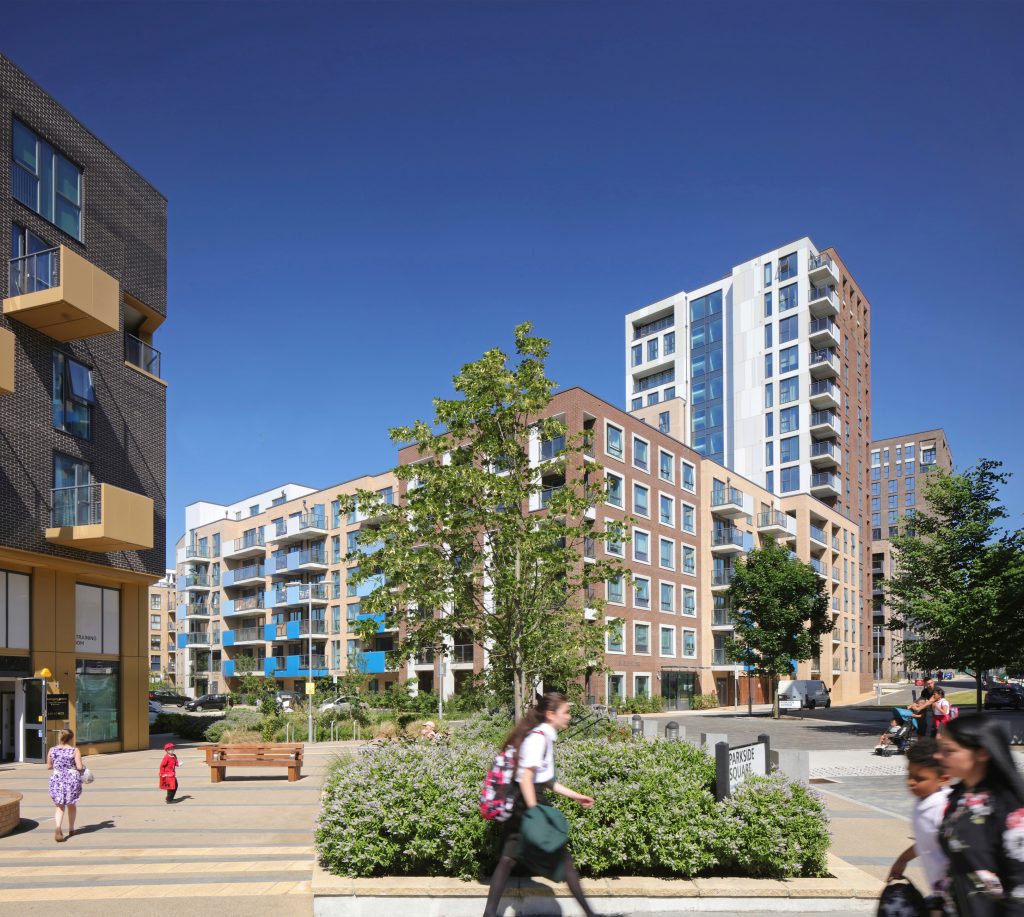

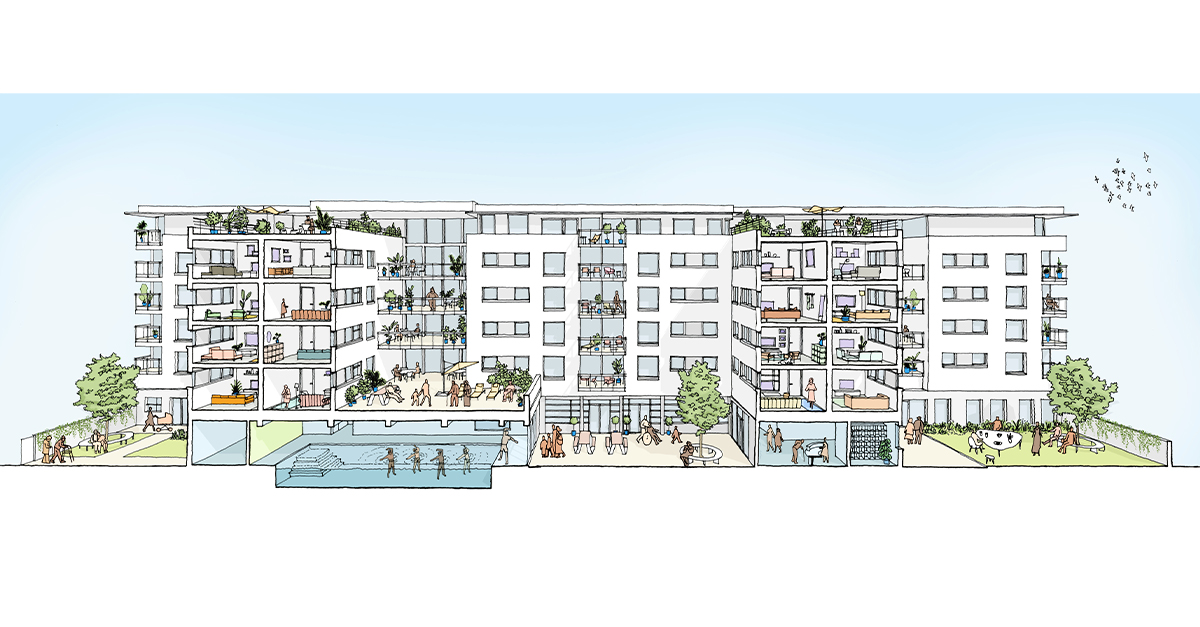
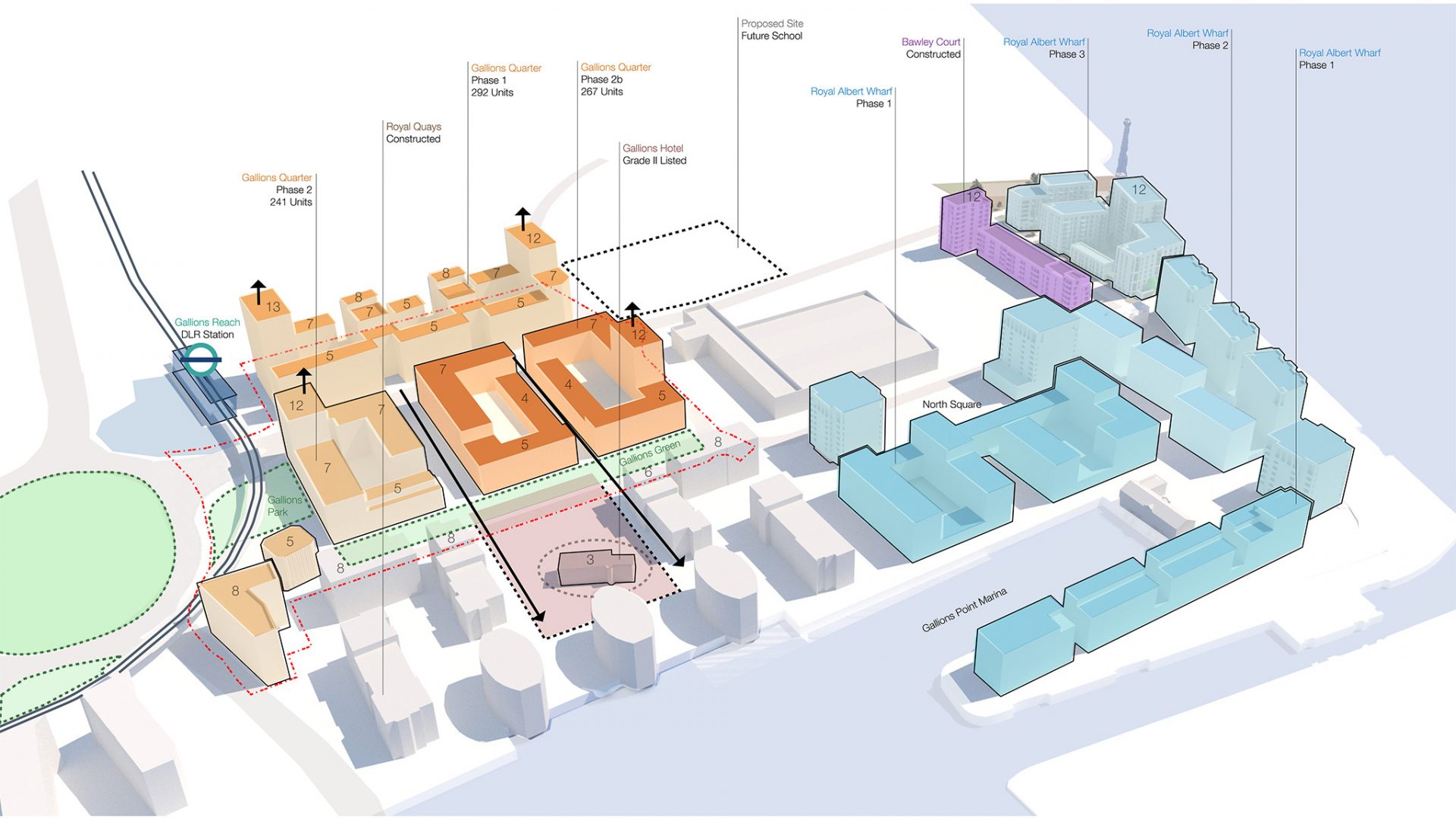
Image: BPTW’s ongoing regeneration of the Heathside and Lethbridge Estate, Lewisham© Ben Luxmoore.